Did Your Urinary Infection Come From a Chicken Coop?
Blog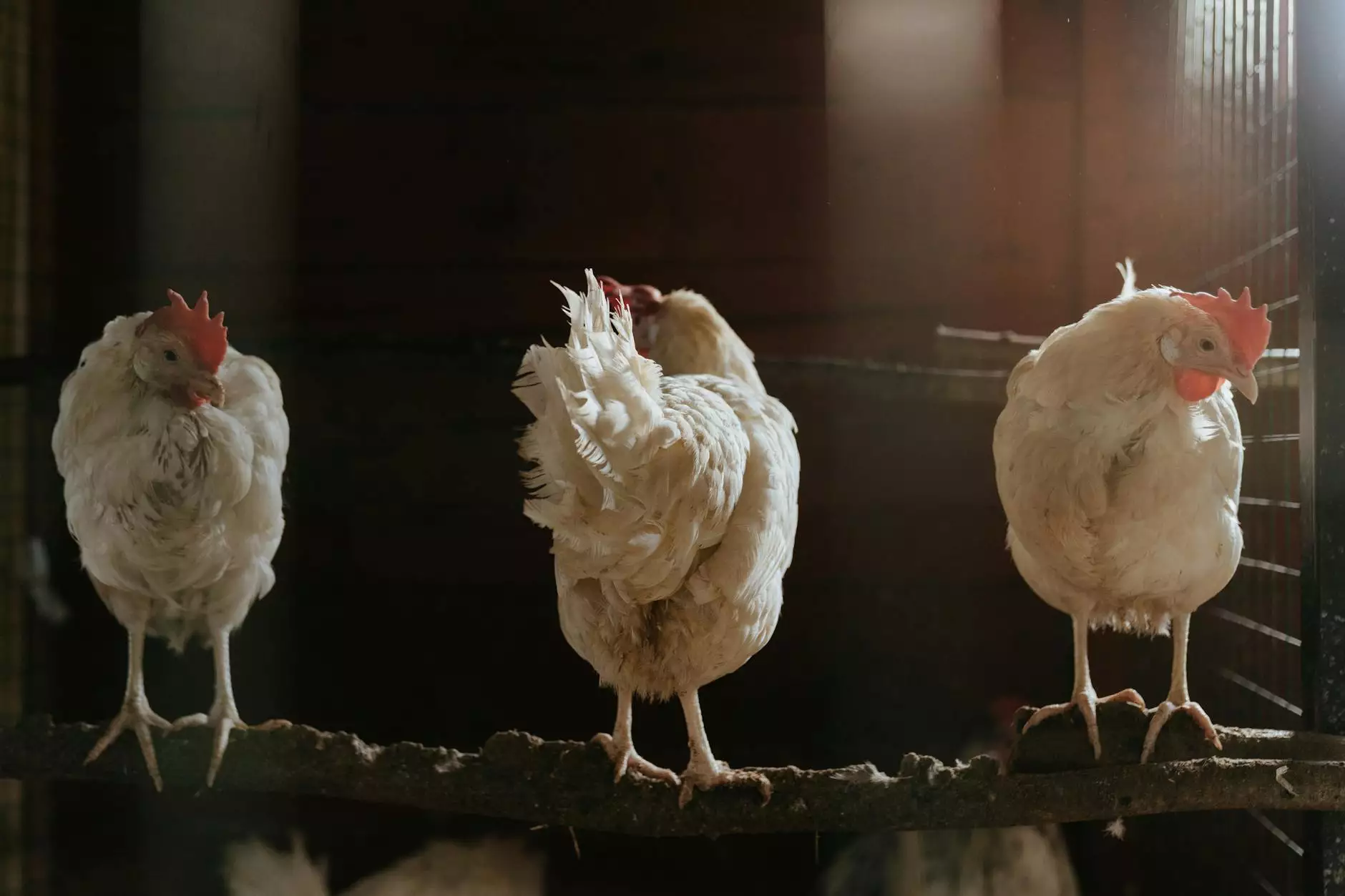
Welcome to Bowling Orthopaedics, your reliable source for health information. In this article, we will explore the surprising connection between urinary infections and chicken coops. We will discuss how exposure to chicken coops can lead to urinary infections, and provide valuable tips on prevention and treatment.
The Link Between Chicken Coops and Urinary Infections
Urinary infections, also known as urinary tract infections (UTIs), are caused by bacteria that enter the urinary system. While the most common causes of UTIs are poor hygiene, dehydration, and sexual activity, recent studies have revealed an unexpected connection between UTIs and chicken coops.
When chickens and other poultry are kept in close proximity to human living spaces, the risk of bacterial transmission increases. Chicken droppings contain harmful bacteria such as E. coli and Salmonella, which can contaminate the surrounding environment, including soil and water sources. If individuals come into contact with these contaminated areas, they may unknowingly transfer bacteria to their urinary tract, leading to a urinary infection.
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risk of urinary infections associated with chicken coops, it is crucial to implement preventive measures. Here are some helpful strategies:
- Maintain strict hygiene: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling chickens, their eggs, or any equipment used in the coop. Encourage regular handwashing for anyone involved in chicken-related activities.
- Wear protective clothing: When working in chicken coops, consider wearing gloves, long sleeves, and closed-toe shoes to minimize direct contact with bacteria-laden surfaces.
- Keep coops clean: Regularly clean and disinfect chicken coops, removing droppings, feathers, and other potential sources of bacteria. This will help reduce the bacterial load and decrease the risk of infection.
- Avoid cross-contamination: Ensure that food and water sources for humans are kept separate from those of the chickens, preventing the transfer of bacteria between species. Use separate utensils and containers for chicken-related tasks.
- Proper waste disposal: Dispose of chicken waste appropriately, following local guidelines. Do not use chicken waste as fertilizer for vegetable gardens or allow it to contaminate water sources.
Treatment Options
If you suspect a urinary infection linked to chicken coop exposure, it is important to seek medical assistance. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend suitable treatment options, which may include:
- Antibiotics: Prescription antibiotics are commonly used to treat urinary infections. It is crucial to take the full course of medication as prescribed to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria.
- Increased fluid intake: Drinking plenty of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary system, aiding in the recovery process.
- Urinary analgesics: These medications can provide relief from pain and discomfort associated with urinary infections.
- Probiotics: Some studies suggest that probiotics may help restore healthy bacteria levels in the urinary tract and reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while it may sound surprising, there is indeed a connection between urinary infections and chicken coops. By implementing proper hygiene practices, maintaining cleanliness, and seeking medical assistance when necessary, you can reduce the risk of urinary infections associated with exposure to chicken coops. Remember, prevention is key. Stay informed, stay safe, and prioritize your health at Bowling Orthopaedics.
Disclaimer: The information provided on this website is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.