Diet May Help Fight Epilepsy When Meds Fail
Blog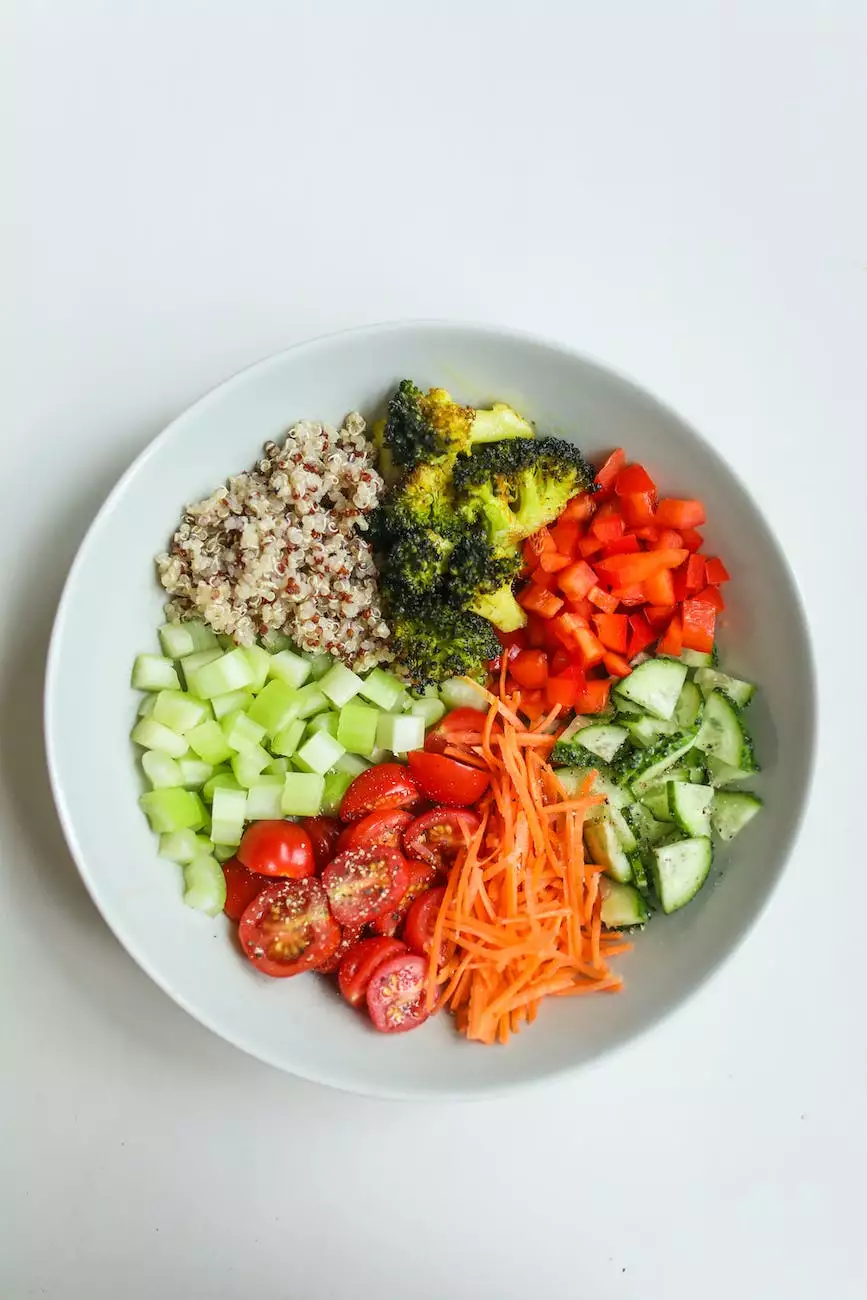
The Role of Diet in Epilepsy Management
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures. While many individuals with epilepsy can effectively control their seizures with medications, there is a proportion that experiences treatment-resistant seizures. For those whose seizures cannot be adequately managed with medications, exploring alternative treatment options becomes crucial.
Introduction to Dietary Therapy
Dietary therapy has gained significant attention as a potential adjunctive or even primary treatment approach for epilepsy. Many patients have reported positive results when traditional medications have failed to provide adequate seizure control. The key principle that underlies the effectiveness of dietary therapy is the alteration of the body's primary source of energy - glucose - to a different source, such as ketones.
Ketogenic Diet
The Ketogenic Diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and moderate-protein diet that has shown promising results in reducing seizure frequency among individuals with epilepsy. It induces a state of ketosis in the body, in which ketone bodies become the primary source of energy instead of glucose. The diet follows a specific macronutrient ratio, typically consisting of 70-90% fat, 5-10% carbohydrates, and 5-15% protein.
How Does the Ketogenic Diet Work?
When the body is in a state of ketosis, it produces ketone bodies from fatty acids to fuel the brain and other organs. Ketones provide a more stable and efficient energy source, leading to a potential reduction in seizure activity. Additionally, the Ketogenic Diet influences various neurochemical and metabolic changes in the brain, leading to improved seizure control.
Modified Atkins Diet (MAD)
The Modified Atkins Diet (MAD) is another low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that shares similarities with the Ketogenic Diet. However, MAD allows for slightly more carbohydrates and protein intake, making it a more flexible alternative. It has shown promise in reducing seizures, particularly in adolescents and adults with epilepsy.
Incorporating Dietary Therapies Into Epilepsy Management
Before initiating any dietary therapy, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in epilepsy management. They can provide guidance on the appropriate diet plan, considering an individual's specific needs and medical history. It is important to note that dietary therapies require strict adherence and close monitoring to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Benefits and Limitations of Dietary Therapy
Dietary therapy offers numerous benefits for individuals with treatment-resistant epilepsy when medications fail. Some potential benefits include:
- Reduction in seizure frequency: Many patients experience a significant decrease in seizure frequency or complete seizure control.
- Improved cognitive function: Some individuals report improved cognition and alertness after following a specialized diet.
- Reduced reliance on medication: Dietary therapy may allow for a reduction in antiepileptic medication dosages under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
- Minimal side effects: Compared to some medications, dietary therapies generally have fewer side effects.
Despite these potential benefits, it is important to recognize the limitations of dietary therapy:
- Dietary restrictions: Patients must adhere to strict dietary guidelines and may need to limit or avoid certain foods.
- Potential nutrient deficiencies: Some diets may require additional vitamin and mineral supplementation to ensure nutritional balance.
- Difficulty in adherence: Dietary therapies can be challenging to follow long-term, requiring commitment and discipline.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when traditional medications fail to adequately manage epilepsy, dietary therapy can be a potential alternative. The Ketogenic Diet and Modified Atkins Diet have shown promising results in reducing seizure frequency and improving overall seizure control. Consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in epilepsy management is crucial before embarking on any dietary therapy. They can guide individuals through the process, address concerns, and monitor progress.